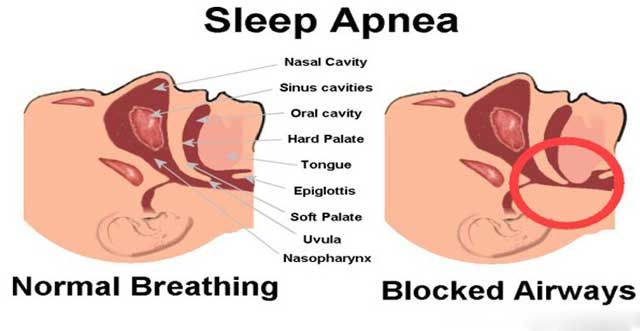
Sleep Apnea means that one stops breathing during sleep. A significant number of people do not know they have sleep apnea, and many people don’t know for a long time when a family member or friend points it out. Unfortunately, sometimes people develop a serious health complication from it.
Symptoms that can occur :
- Loud snoring
- Episodes in which you stop breathing during sleep — which would be reported by another person
- Gasping for air during sleep
- Awakening with a dry mouth
- A morning headache
- Difficulty staying asleep (insomnia)
- Excessive daytime sleepiness (hypersomnia)
- Difficulty paying attention while awake
- Irritability
If left untreated, sleep apnea can lead to health problems. Although your body will force a deep breath eventually, people with sleep apnea can go 10 seconds or more without breathing, up to 100 times an hour in the most severe cases.
During regular sleep, we go through 4 cycles of sleep. Two cycles of light sleep and two cycles of deep sleep. Various cycles can affect the brain waves which can cause the waves to change and signify dream states or periods of deep sleep.

Sleep apnea disrupts regular sleep. If long periods of apnea occur at night, your brain must send a message to your body to get out of sleep to take a deep breath. Most people do not remember this occurring, but the disruption of sleep is so strong that it will trigger you to go from deep sleep to light sleep.
The main types of sleep apnea are:
- Obstructive sleep apnea,the more common form that occurs when throat muscles relax
- Central sleep apnea,which occurs when your brain doesn’t send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing
- Complex sleep apnea syndrome,also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, which occurs when someone has both obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a serious medical condition. Complications can include:
- Daytime fatigue.The repeated awakenings associated with sleep apnea make normal, restorative sleep impossible, which may lead to severe daytime drowsiness, fatigue, and irritability.
You might have difficulty concentrating and find yourself falling asleep at work, while watching TV, or even when driving. People with sleep apnea have an increased risk of motor vehicle and workplace accidents.
You might also feel quick-tempered, moody, or depressed. Children and adolescents with sleep apnea might perform poorly in school or have behavior problems.
- High blood pressure or heart problems.Sudden drops in blood oxygen levels that occur during sleep apnea increase blood pressure and strain the cardiovascular system. Having obstructive sleep apnea increases your risk of high blood pressure (hypertension).
Obstructive sleep apnea might also increase your risk of recurrent heart attack, stroke, and abnormal heartbeats, such as atrial fibrillation. If you have heart disease, multiple episodes of low blood oxygen (hypoxia or hypoxemia) can lead to sudden death from an irregular heartbeat.
- Type 2 diabetes.Having sleep apnea increases your risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Metabolic syndrome.This disorder, which includes high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels, high blood sugar, and an increased waist circumference, is linked to a higher risk of heart disease.
- Complications with medications and surgery.Obstructive sleep apnea is also a concern with certain medications and general anesthesia. People with sleep apnea might be more likely to have complications after major surgery because they’re prone to breathing problems, especially when sedated and lying on their backs.
Before you have surgery, tell your doctor about your sleep apnea and how it’s being treated.
- Liver problems.People with sleep apnea are more likely to have abnormal results on liver function tests, and their livers are more likely to show signs of scarring (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease).
- Sleep-deprived partners.Loud snoring can keep anyone who sleeps near you from getting good rest. It’s not uncommon for a partner to have to go to another room, or even to another floor of the house, to be able to sleep.
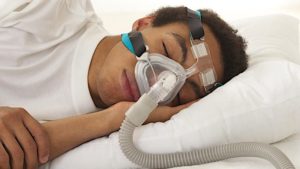
Doctors will prescribe CPAP devices, and also oxygen use for nighttime sleeping. Your doctor will choose the best treatment for your apnea. Many of our patients who suffer from Apnea use the following for their treatment :





0 Comments